6.11.4 An Animated Robot ArmIn this example we will define fixed positions for all the finger-tips and a motion for the wrist. 1. Create three offset primitives under the root level. We will use these offsets for defining fixed positions for the finger-tips. The reason why we create the offsets above the arm level is that when we animate the arm, it should not animate these offsets (because we want that they stay fixed). 2. Create an INVERSE KINEMATICS method under the skeleton method of each finger. 3. Create a link to each offset and Cut&Paste it under the corresponding INVERSE KINEMATICS method. 4. Create an INVERSE KINEMATICS method under the skeleton method used for controlling the entire arm, and create a B-Spline curve defining a motion for the wrist, under the new method. |
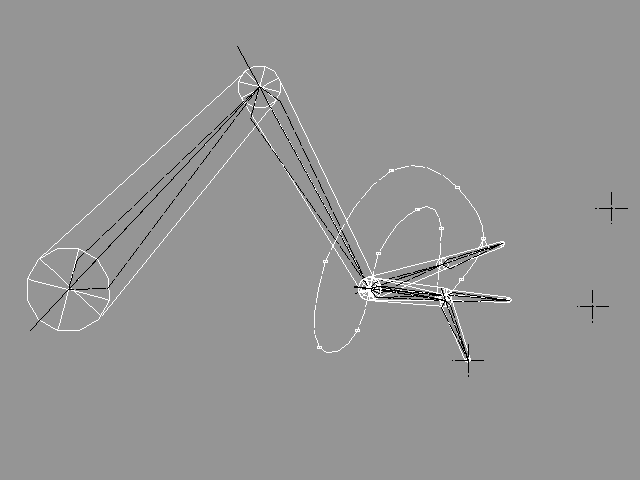 YouTube Figure T6-35: A Skeletonally controlled arm. The wrist is moving, while the finger-tips and the shoulder remain fixed. |
|
Before we leave these Inverse Kinematics examples, it should be noted that examples we have gone through so far could only scratch the surface of all the possibilities which inverse kinematics and skeletonal control offer. For example, they are very important tools when animating mechanical devices, such as engines of cars and especially when building up mechanical connections. |
| ghh don'tpanic |